Just over three months after US-based aerospace start-up Muon Space launched its FireSat Protoflight satellite, the end-to-end space systems provider has shared the first images taken by the spacecraft.
This spacecraft, launched on SpaceX’s Transporter-13 mission in March, was a collaboration between Muon, and Earth Fire Alliance, a non-profit organisation aiming to gather real-time data from all fires on Earth.
“These first light images confirm that our IR sensors are operating as designed and collecting high-quality data,” said Dan McCleese, chief scientist of Muon Space in a press release.
The FireSat Protoflight satellite is the first of a proposed 50 satellites that Muon aims to launch, which they aim to use to track wildfires on Earth. The first few images taken by the FireSat Protoflight have been from a low-Earth orbit, using a multi-band infrared (IR) instrument. This then scanned for heat signatures, which could indicate the presence of wildfires.
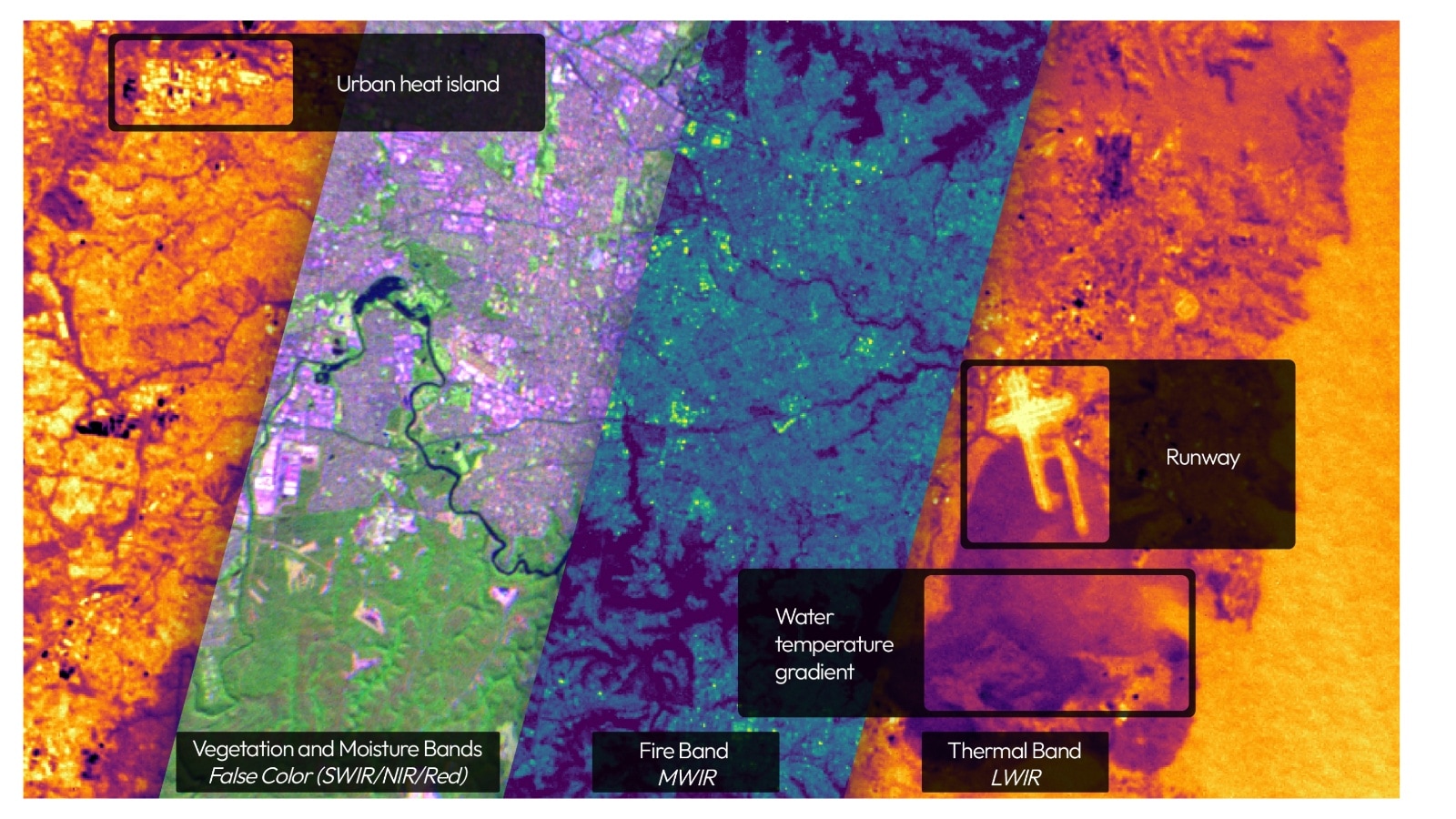
Using a precise high-dynamic range (HDR) six-channel multispectral IR instrument, the satellites are capable of multispectral imaging across the visible, near-infrared (NIR), short-wave infrared (SWIR), mid-wave infrared (MWIR), and long-wave infrared (LWIR) bands simultaneously. Each band takes up a channel, and the channels are used together to derive further information. The instrument is built by Muon Space itself.
The satellites are able to scan areas of over 1,500 kilometres at a time, and identify fires as small as five-by-five meters in that range. They are also able to make a distinction between false positive fires and actual wildfire threats.
 (Image credit: Muon Space)
(Image credit: Muon Space)
The above image depicts FireSat Protoflight detecting thermal signatures at Libya’s Sarir oil field complex, which are likely gas flares rather than a wildfire risk. The satellite’s channels observing MWIR and LWIR identify the same heat sources, indicating the effectiveness of the multi-channel approach in data collection and allowing FireSat to differentiate different types of heat sources and confirm detections.
Story continues below this ad
Once relevant data is acquired, it is sent out to first responders, policymakers, and communities facing escalating wildfire threats. This is a crucial advancement in space-based wildfire monitoring, providing accurate and relevant information to governments and concerned citizens alike.
Muon is set to launch the first block of three further FireSat satellites in 2026, and aims for the FireSat constellation to be at capacity and fully operational by 2030. The constellation is set to have global coverage, and will scan the entirety of Earth for wildfires every twenty minutes. Wildfire-prone areas would be scanned even more often, to further reduce the threat.
(This article has been curated by Purv Ashar, who is an intern with The Indian Express)




Average Rating